Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a diagnostic imaging procedure used to examine the uterus and fallopian tubes. It involves the use of X-rays and a contrast dye to visualize the internal structures of the reproductive system. Healthcare professionals commonly perform HSG to assess the fallopian tubes for blockages or abnormalities and to investigate the cause of infertility or recurrent miscarriages. Here’s an explanation of how the HSG procedure works and why it’s used:
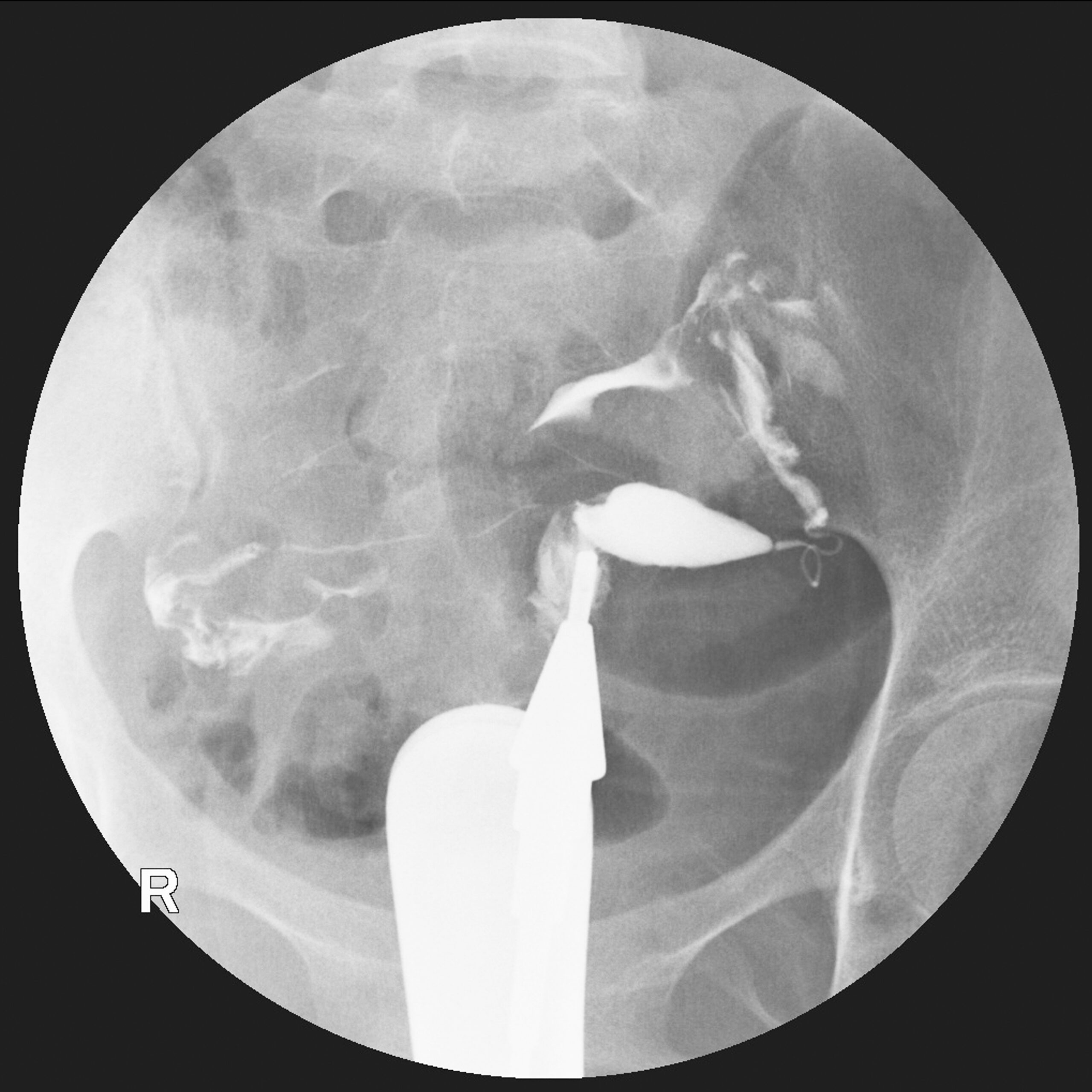
Procedure Of Hysterosalpingography:
During a hysterosalpingography procedure:
Preparation: Before the procedure, your healthcare provider may recommend taking a pain reliever to minimize discomfort. You’ll also receive advice to empty your bladder.
Positioning: You will lie on an examination table, similar to a pelvic exam.
Speculum Insertion: Speculum for the vagina to visualize the cervix.
Catheter Insertion: Gently insert a thin catheter through the cervix and into the uterus.
Contrast Injection: A contrast dye is injected through the catheter into the uterus. The dye helps outline the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes, making them visible on X-ray images.
X-ray Imaging: Capture X-ray images as the contrast dye fills the uterus and flows into the fallopian tubes.
Fluoroscopy: Utilize real-time X-ray images (fluoroscopy) to observe the movement of the contrast dye.
Purpose:
Hysterosalpingography is performed for various reasons:
Fallopian Tube Evaluation: The procedure helps assess the fallopian tubes for blockages, structural abnormalities, or scarring that might hinder the passage of eggs or sperm.
Infertility Assessment: Healthcare professionals commonly use HSG to investigate the cause of infertility by identifying potential issues with the fallopian tubes or uterine cavity.
Recurrent Miscarriages: HSG can help identify abnormalities that might contribute to recurrent miscarriages.
Uterine Abnormalities: The procedure can reveal uterine abnormalities such as polyps, fibroids, or other structural issues.
Guiding Treatment: HSG results can guide treatment decisions, such as fertility treatments or surgical interventions.
Discomfort and Risks Of Hysterosalpingography:
HSG can cause mild discomfort, similar to menstrual cramps, during the procedure. Some women may experience temporary spotting or cramping afterward. Rarely, there is a risk of infection or allergic reaction to the contrast dye.
Interpreting Results:
After the procedure, a radiologist or healthcare provider analyzes the X-ray images. They can identify and discuss abnormalities or blockages in the fallopian tubes or uterine cavity with the patient.
Hysterosalpingography is a valuable diagnostic tool in reproductive medicine, providing insights into the health of the fallopian tubes and uterus. Healthcare professionals often recommend it as part of the infertility evaluation process to help determine the best course of treatment for individuals experiencing difficulties with conception or recurrent pregnancy loss.


