Laparoscopy, also known as minimally invasive surgery or keyhole surgery, is a surgical technique used in gynecology to diagnose and treat various conditions within the abdominal and pelvic cavities. It involves making small incisions and inserting a thin, lighted instrument called a laparoscope through one of the incisions. This allows the surgeon to visualize the internal organs and perform procedures with specialized surgical instruments. Here’s how laparoscopy is used in gynecology:
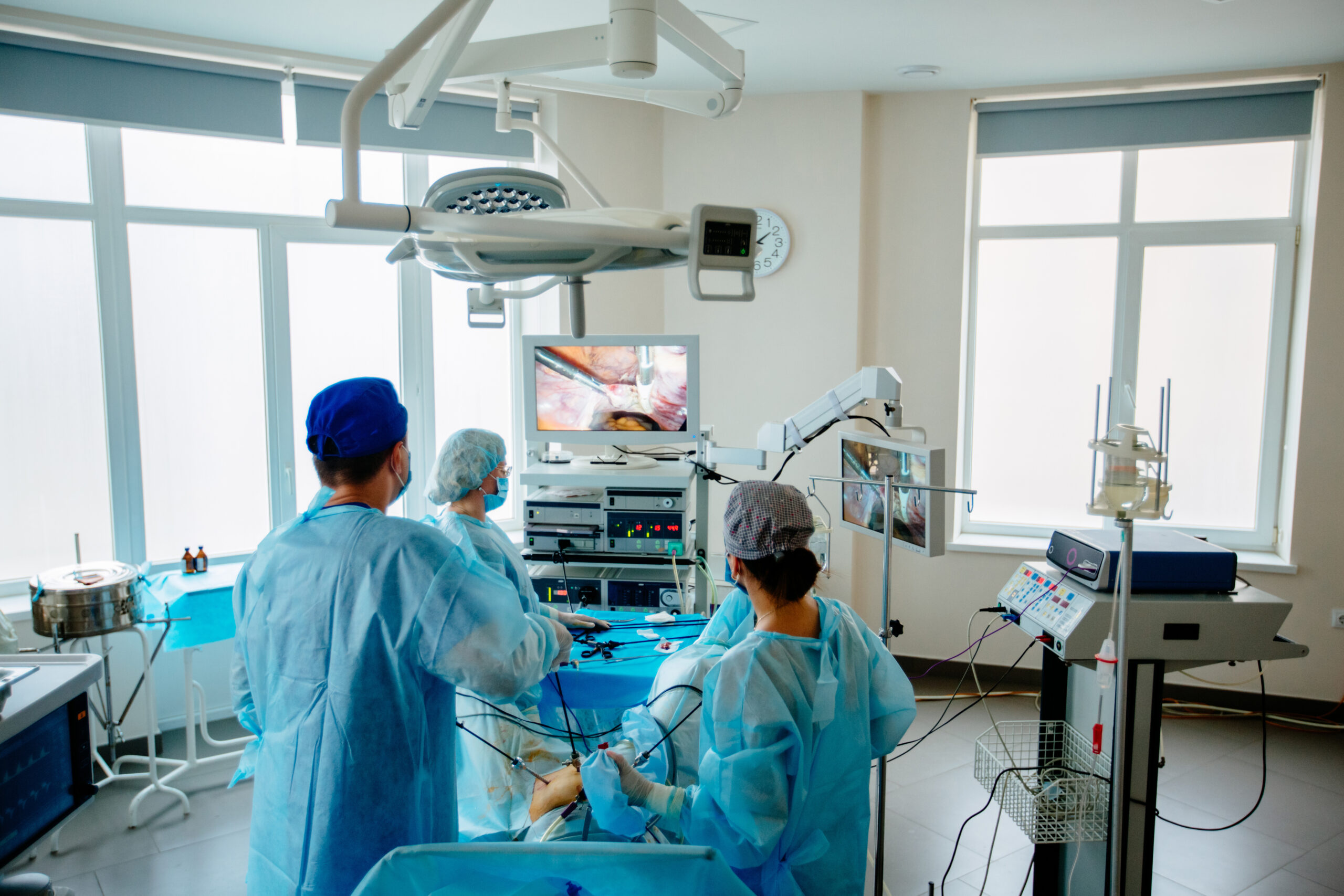
Procedure Of Laparoscopy:
During a laparoscopy procedure:
Anesthesia: General anesthesia is administered to ensure the patient is asleep and comfortable during the surgery.
Incision: A few small incisions (usually less than an inch) are made near the surgical area, through which the laparoscope and other instruments are inserted.
Laparoscope Insertion: The laparoscope, which has a camera and light source, is inserted through one of the incisions. It transmits images to a monitor, allowing the surgeon to see inside the body.
Visualization: The surgeon views the images on the monitor to assess the condition and anatomy of the pelvic and abdominal organs.
Surgical Procedures: Additional instruments can be inserted through the other incisions to perform procedures such as removing cysts, treating endometriosis, removing fibroids, performing hysterectomy, and more.
Closure: After completing the procedures, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive strips.
Applications in Gynecology:
Laparoscopy is used for various gynecological purposes:
Diagnosis: Laparoscopy is a valuable tool for diagnosing conditions such as endometriosis, ovarian cysts, pelvic inflammatory disease, and adhesions.
Endometriosis Treatment: Laparoscopy allows for the removal of endometriotic lesions, reducing pain and improving fertility.
Ovarian Cyst Removal: Laparoscopy can be used to remove ovarian cysts and assess the health of the ovaries.
Hysterectomy: Laparoscopic hysterectomy involves removing the uterus through small incisions, resulting in a faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery.
Myomectomy: Laparoscopic myomectomy removes fibroids from the uterus while preserving fertility.
Tubal Ligation: Laparoscopic sterilization (tubal ligation) involves sealing or blocking the fallopian tubes for permanent contraception.
Ectopic Pregnancy: Laparoscopy can treat ectopic pregnancies by removing the pregnancy from the fallopian tube.
Advantages Of Laparoscopy:
Minimally Invasive: Laparoscopy requires smaller incisions, resulting in less pain, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery compared to open surgery.
Reduced Scarring: Small incisions lead to minimal scarring compared to traditional open surgery.
Shorter Hospital Stay: Patients usually experience shorter hospital stays and quicker return to normal activities.
Less Blood Loss: Typically involves less blood loss compared to open surgery.
Considerations:
While laparoscopy offers numerous benefits, it’s important to note that it’s not suitable for all cases, and the decision to use this technique depends on the specific condition, patient factors, and surgeon’s expertise. Risks and potential complications, though rare, include infection, bleeding, injury to surrounding structures, and anesthesia-related complications.
Laparoscopy is a valuable tool in gynecology, providing surgeons with the ability to perform complex procedures with minimal invasiveness and enhanced visualization. It has revolutionized gynecological surgery and improved patient outcomes and experiences.


